b<>com showed new software at IBC for content creators/providers pursuing content security and HDR conversion, and announced Ateme as a member investor in their Research Institute.

At IBC, b<>com showed two new software tools for content creators and providers interested in content security and HDR conversion, and made a further announcement that Ateme has become a member investor in b<>com’s Technological Research Institute (IRT).
*Tag* Content ID Tracking
*Tag* is a stand-alone invisible digital watermarking tool that audiovisual creators can use to track and verify the integrity of their content, and as a way to detect and combat disinformation and deepfakes. It is integrated throughout the audiovisual creation and supply chain from production to distribution and, because no metadata or connection to the cloud are required, users can address piracy for both live and VOD content. *Tag* can certify that content has not been digitally altered and is authentic.
The team at b<>com has been working with Viaccess-Orca (VO) to develop a dynamic watermarking approach that addresses the range of piracy threats that broadcasters face and makes it possible to directly identify the source of the piracy. Through the collaboration, b<>com has supplemented its skill and experience in cybersecurity with VO’s expertise in content protection and pirate stream analysis.
Real-Time Digital Marking
Their *Tag* software, based on flexible tracking algorithms, enables the real-time digital marking of video streams, including 4K formats, regardless of what device is used - TV decoder, tablet, smartphone or web player. Its algorithms are able to resist a variety of piracy attacks, such as camcording, strong lossy compression and collusions. VO has now adopted *Tag* to combat the piracy of video streams from live sporting events.
Using VO’s Dynamic Watermarking, for instance, among the services in the VO Anti-Piracy Center, content owners can launch VOD and live campaigns and quickly identify the source of piracy. By also developing their applications with VO secure video player, operators can integrate the watermarking on the client side, which is more cost-effective than server-side watermarking.

Verification
The digital watermark b<>com developed adds a unique, indelible, invisible digital mark to video content or images. Among its applications, video authentication ensures that no deepfakes are present and that the content offered is the original.
b<>com recognises the damage that deepfakes can cause, ranging from scams of all kinds and manipulation of information, to influencing public opinion. In the race between the developments in generating deepfakes – which the human eye can hardly differentiate from reality – and those for detecting them, digital watermarking is regarded as a formidable tool. It can certify that video content has not been altered – and in particular, that no malicious processing has occurred – and that it is entirely authentic.
Gaëtan Le Guelvouit, cybersecurity specialist at b<>com, sees verification as a critical application for *Tag*. “It verifies that all the images in a video are present and intact and that no faces or elements have been replaced or erased,” he said. “Because it can be used anywhere in the content production chain, from camera capture to broadcast, it can suit camera manufacturers, who can include it directly in their devices, as well as editing software publishers, transcoder manufacturers or SaaS solutions – all can take advantage of this kind of detection."
Testing
“Operating as a stand-alone system, *Tag* becomes easy to adopt and integrate. It requires no connection to an external server, exchange of information or sending metadata to the cloud. *Tag* operates autonomously, which greatly simplifies its adoption and integration and keeps its power consumption low,” Gaëtan said.
Cartesian, a consulting firm specialising in telecommunications, media and technology, tested the robustness of the solution through its Farncombe Security Audit Watermark, which is developed according to specifications set by the Hollywood movie industry. During the audit, largely due to its live-optimized analysis algorithm, the technology passed all the robustness tests, which check the watermark’s ability to withstand attempts to obfuscate it or prevent it from being recovered.
AI-based Implementation for *Sublima* HDR Conversion
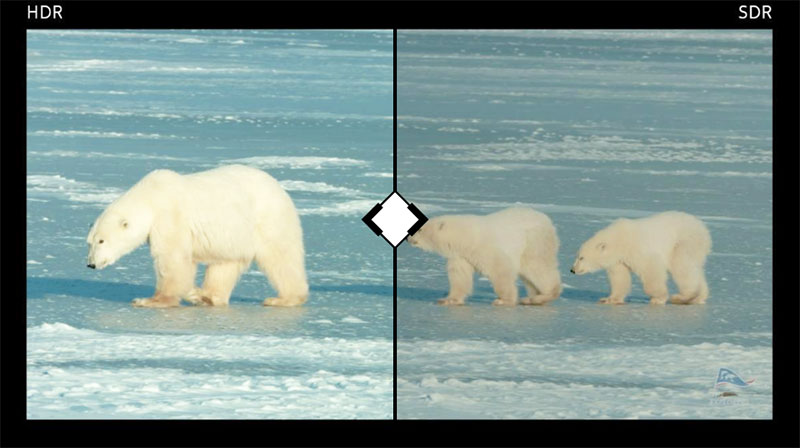

b<>com has introduced a new AI-driven feature to its *Sublima* HDR converter, which has been commercialised and, so far, integrated into the video processing equipment of numerous partners such as EVS, Apantac and Harmonic. The *Sublima* IP Core was shown at IBC with a new, more efficient AI-based implementation using the NPU in a SoC chip from Synaptics, enabling it to diversify its use to the new generation of set-top boxes.
NPUs accelerate deep learning algorithms by natively and efficiently executing specific operations that neural networks rely on. NPUs are a custom-built alternative to purpose-building the framework for running such operations, or running environments that support the associated computations. GPUs are actually capable of AI operations as well, but generally consume a lot of power – a GPU may be faster than an NPU at computing a given set of AI tasks, but an NPU will use much less power than a GPU on the same tasks.
Simpler Workflows
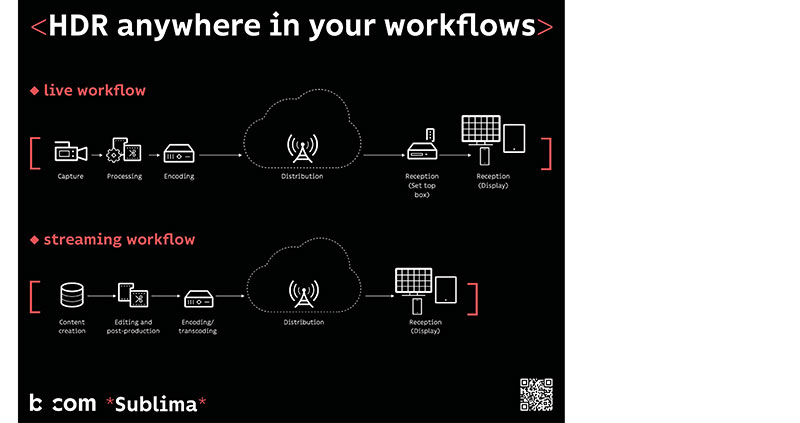
Like *Tag*, *Sublima* can be used at any stage of the workflow from production to distribution, in local video processing equipment or cloud infrastructures, as well as in set-top boxes or smart TVs. It means operators can preserve the artistic intent of content owner, and the owners can make HDR available across their catalogues at low cost.
Workflows are simpler because SDR to HDR/HDR to SDR conversions can be combined, and can include live production, as the software does not require metadata and is context-aware. It also works automatically – users do not need to select parameters, preserve extra data for HDR10 or have specialised expertise. It works with any HDR format – PQ, HLG and Slog3.
Now, on top of availability on FPGA, CPU and GPU on components from Altera, Intel and AMD, as mentioned, the Synaptics SoC chip enables developers to extend its use to newer set-top-boxes.
Ateme Joins b<>com’s Technological Research Institute
In the lead-up to IBC, Ateme has become a member investor in b<>com’s Technological Research Institute. Attracted by the value of collaboration between the industry and academics to accelerate innovation, Ateme has joined the IRT to explore new video formats and enhance the user experience, while addressing the challenges of energy efficiency facing the broadcast industry. Reducing the impact of digital innovations is central to the IRT's strategy.
b<>com and the IRT note that video is energy-intensive and currently accounts for more than 70% of telecommunications data. As content quality continues to improve, these volumes are increasing exponentially. To meet the challenge, Ateme and b<>com are joining to develop ways to reduce the carbon footprint of video content, from production to distribution. Their main focus includes improving video compression and gaining efficiency through the use of AI.
Ateme also expects to benefit from the IRT's capabilities in creating new technological standards and draw on its ability to unite expertise from academic and industry communities. b-com.com
Images: @b<>com